- ImageCLEF 2025
- LifeCLEF 2025
- ImageCLEF 2024
- LifeCLEF 2024
- ImageCLEF 2023
- LifeCLEF 2023
- ImageCLEF 2022
- LifeCLEF2022
- ImageCLEF 2021
- LifeCLEF 2021
- ImageCLEF 2020
- LifeCLEF 2020
- ImageCLEF 2019
- LifeCLEF 2019
- ImageCLEF 2018
- LifeCLEF 2018
- ImageCLEF 2017
- LifeCLEF2017
- ImageCLEF 2016
- LifeCLEF 2016
- ImageCLEF 2015
- LifeCLEF 2015
- ImageCLEF 2014
- LifeCLEF 2014
- ImageCLEF 2013
- ImageCLEF 2012
- ImageCLEF 2011
- ImageCLEF 2010
- ImageCLEF 2009
- ImageCLEF 2008
- ImageCLEF 2007
- ImageCLEF 2006
- ImageCLEF 2005
- ImageCLEF 2004
- ImageCLEF 2003
- Publications
- Old resources
You are here
Domain adaptation
Welcome to the website of the Domain Adaptation challenge!
Schedule
- 01.11.2013: Registration opens (register here)
- 23.12.2013: Development data is released (instructions to access the data)
- 20.04.2014: Test data is released (download here)
- 20.04.2014: Submission system opens (instructions for submission)
- 04.05.2014: Submission system closes
- 10.05.2014: Processed submission results are released. The winner is the XRCE (Xerox Research Centre Europe) group.
- 07.06.2014: Deadline for submission of working notes papers
- 15.-18.09.2014: CLEF 2014, Sheffield, UK
Task overview
The amount of freely available and annotated image collections is dramatically increased over the last years, thanks to the diffusion of high-quality cameras, and also to the introduction of new and cheap annotation tools such as Mechanical Turk. Attempts to leverage over and across such large data sources has proved challenging. Indeed, tools like Google Goggle are able to recognize reliably limited classes of objects, like books or wine labels, but are not able to generalize across generic objects like food items, clothing items and so on. This problem is known in the literature as the domain adaptation challenge. Addressing this issue would have a tremendous impact on the generality and adaptability of any vision-based annotation system. Current research in domain adaptation focuses on a scenario where (a) the prior domain (source) consists of one or maximum two databases (b) the labels between the source and the target domain are the same, and (c) the number of annotated training data for the target domain are limited. The goal of this challenge is to push the state of the art towards more realistic settings, relaxing these assumptions. In the 2014 edition, we will focus on the assumption (a), with the number of source data will range from 2 up to at least 5. Participants will be asked to build recognition systems for the target classes by leveraging over the source knowledge. Source data will be provided by exploiting existing available resources like the ImageNet, Caltetch256, AwA databases and so on. Target data will be collected from the Web, using existing tools like Google Image or Bing. Performance will be measured in terms of accuracy.
Registering for the task and accessing the data
To participate in this task, please register by following the instructions found in the main ImageCLEF 2014 webpage.
Organizers
- Barbara Caputo, University of Rome La Sapienza, caputo@dis.uniroma1.it
- Novi Patricia, Idiap Research Institute, novi.patricia@idiap.ch
Contact
For any doubt related to the task, please send email to: novi.patricia@idiap.ch
Result
| Final Result Domain Adaptation Challenge |
| # | Group Name | SCORE TOTAL |
| 1 | XRCE | 228 |
| 2 | Hubert Curien lab group | 158 |
| 3 | IDIAP | 45 |
XRCE
| Score per Class |
| # | Score Class | |
| 1 | 41 | |
| 2 | 12 | |
| 3 | 15 | |
| 4 | 18 | |
| 5 | 20 | |
| 6 | 23 | |
| 7 | 17 | |
| 8 | 8 | |
| 9 | 17 | |
| 10 | 28 | |
| 11 | 12 | |
| 12 | 17 |
Hubert Curien lab group
| Score per Class |
| # | Score Class | |
| 1 | 36 | |
| 2 | 7 | |
| 3 | 15 | |
| 4 | 5 | |
| 5 | 25 | |
| 6 | 10 | |
| 7 | 13 | |
| 8 | 8 | |
| 9 | 6 | |
| 10 | 15 | |
| 11 | 7 | |
| 12 | 11 |
IDIAP
| Score per Class |
| # | Score Class | |
| 1 | 3 | |
| 2 | 1 | |
| 3 | 0 | |
| 4 | 4 | |
| 5 | 3 | |
| 6 | 6 | |
| 7 | 7 | |
| 8 | 3 | |
| 9 | 2 | |
| 10 | 3 | |
| 11 | 3 | |
| 12 | 10 |
| Runs |
| # | Group Name | Score Total | Run name |
| 1 | XRCE | 228 | 1399306364121__combin6_Np20_div108 |
| 2 | XRCE | 228 | 1398937484692__combin3_Np18_div108 |
| 3 | XRCE | 226 | 1398938027662__combinAll6_Np19_div164 |
| 4 | XRCE | 217 | 1399306281302__combin6A_Np19_div78 |
| 5 | XRCE | 214 | 1399298355362__MLNCM_MLDA_128_it200_e0.1_Topk1_NCMC5_bigloop_eqw_MV_p025 |
| 6 | XRCE | 212 | 1399305916296__combinAll7A_Np19_div134 |
| 7 | XRCE | 208 | 1399306386958__combin8A_Random_Np25_div78 |
| 8 | XRCE | 185 | 1399298318039__MLNCMC_ML_128_it200_e0.1_Topk1_NCMC1__hsTD_eqw_MV_p025 |
| 9 | XRCE | 182 | 1398937340813__combin2_Np10_div134 |
| 10 | XRCE | 158 | 1399298540326__svmBoost_Mul_Power_f60_acc383 |
| 11 | Hubert Curien lab group | 158 | 1399307327099__Our_Results |
| 12 | Hubert Curien lab group | 142 | 1399282760110__data_label |
| 13 | Hubert Curien lab group | 140 | 1399314094053__results |
| 14 | Hubert Curien lab group | 140 | 1399313194459__results |
| 15 | Hubert Curien lab group | 140 | 1399310150668__results |
| 16 | Hubert Curien lab group | 138 | 1399281473861__data_label |
| 17 | Hubert Curien lab group | 133 | 1399313519232__results |
| 18 | Hubert Curien lab group | 132 | 1399216516740__data_label |
| 19 | Hubert Curien lab group | 77 | 1399311976079__results |
| 20 | IDIAP | 45 | 1399899953697__result_hl2l_svm_c100 |
Download Test Data
Source Domain: (detail) Target Domain: SUNSubmission instructions
The submissions will be received through the ImageCLEF 2014 system, going to "Runs" and then "Submit run" and select track "ImageCLEF2014:domain-adaptation".
Task specific submission instructions and runs format can be seen here.
The task
In this year edition only one task will be considered, where participants should be able to classify images in the target domain by leveraging labeled source data.
The data
Participants are provided with five dataset:
- Caltech-256, consists of 256 object categories with a collection of 30.607 images.
- ImageNet ILSVRC2012, is organized according to the WordNet hierarchy, with an average of 500 images per node.
- PASCAL VOC2012, is image data sets for object class recognition with 20 object classes.
- Bing, contains all 256 categories from Caltech-256 and is augmented with 300 web images per category that were collected through textual search using Bing.
- SUN, is scene understanding database that contains 899 categories and 130.519 images.
- aeroplane
- bike
- bird
- boat
- bottle
- bus
- car
- dog
- horse
- monitor
- motorbike
- people
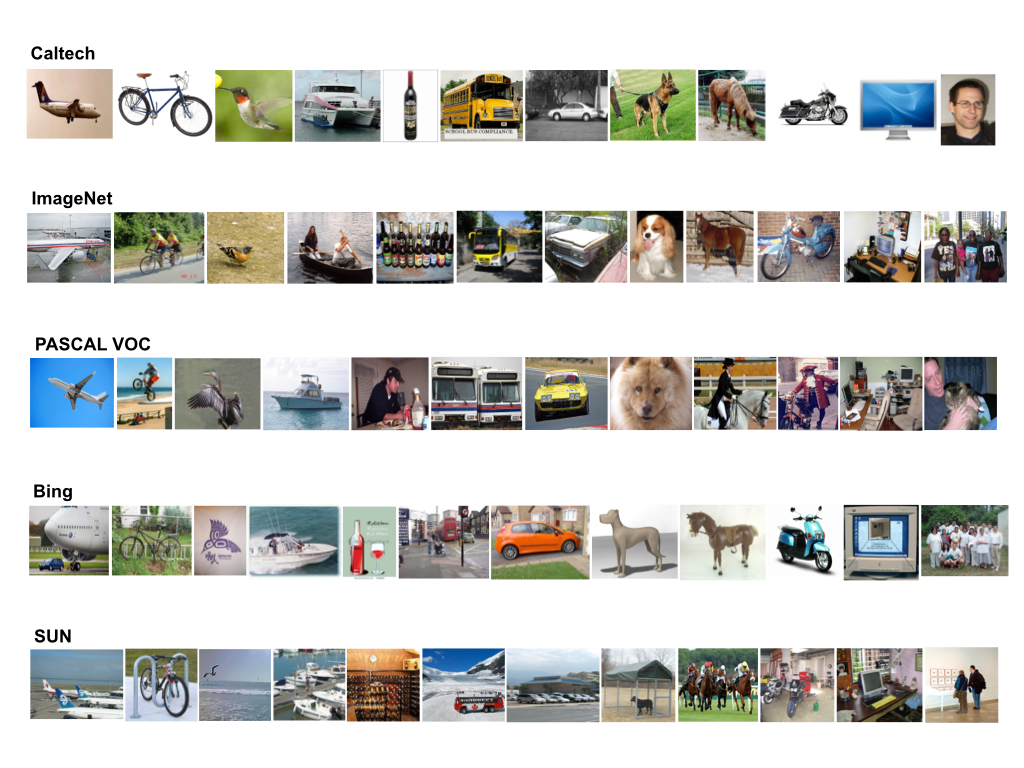
Source Domain
In this year challenge, participants are provided with four source dataset:
- Caltech
- ImageNet
- Pascal
- Bing
Target Domain
The organizers use SUN dataset as target data with 5 images per class for training data and 50 images per class for testing set.
- Training
- Test
Image Feature Extractors
Each image is represented with dense SIFT descriptors (PHOW features) at points on a regular grid with spacing 128 pixels. At each grid point the descriptors are computed over four patches with different radii, hence each point is represented by four SIFT descriptors. The dense features are vector quantized into 256 visual words using k-means clustering on a randomly chosen subset of the Caltech-256 database. Finally, all images are converted to 2x2 spatial histograms over the 256 visual words, resulted in 1024 feature dimension. The software for image extractor is available at www.vlfeat.org.
Reference:- Image Classification using Random Forests and Ferns, A. Bosch, A. Zisserman, X. Munoz, IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2007.
Performance Evaluation
For each image, participants have to provide the class name. The result will be compared with the truth label.
- For each correctly classified image will receive 1 point.
- For each misclassified image will receive 0 point.
Performance Evaluation Script
A matlab script is provided for evaluating performance of the algorithms on the test dataset. The script has been tested under matlab (ver 8.1.0.64) and octave (ver 3.6.2):
Both software are available for Unix/Linux, Windows, and Mac OSX. Octave can be downloaded from http://www.gnu.org/software/octave/download.html. Participants are not required to have knowledge about matlab or octave to run the script. In order to run to script, it needs two files: label.txt and result.txt. 'label.txt' is a file containing the truth label of the test data. Participants need to provide 'result.txt' and can change the filename in the script. In the attachment file contains 3 files:- domainadapt.m
- label.txt
- exampleresult.txt
When using the script, the following codes should be used to represent a class name (case-sensitive):
- aeroplane
- bike
- bird
- boat
- bottle
- bus
- car
- dog
- horse
- monitor
- motorbike
- people
Given that Matlab or Octave is already installed, running the script will produce the following note:
/===============================================\
Domain Adaptation @ImageCLEF 2014
Performance Evaluation Script
\===============================================/
Counting the score
Score per class:
1. 4
2. 2
3. 0
4. 1
5. 2
6. 4
7. 10
8. 5
9. 6
10. 6
11. 3
12. 5
Total score: 48
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| 1.05 MB | |
| 945.31 KB | |
| 1.05 MB | |
| 1.08 MB | |
| 85.96 KB | |
| 864.99 KB |
